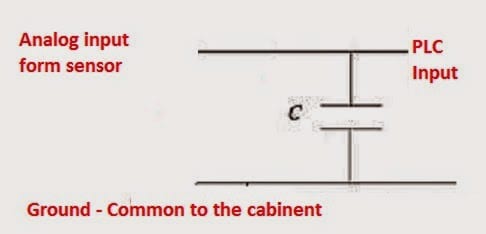
Wiring Interposing Relays – NPN PNP Isolation
We will now look at wiring interposing relays to connect an NPN and PNP sensors into the PLC. Interposing relay means a device that will separate two different circuits. The isolation can be for current consumption, voltage differences, voltage references, or a combination of both current and voltage. We can use these relays to help … Read more