This introduction to IoT Industry 4.0 overviews the concepts and practical approach to the Industrial Internet of Things. Industry 4.0 builds on the digital revolution brought by Industry 3.0, which introduced computers like PLCs to the manufacturing floor and took us to the next level of technological advancement. The Internet of Things (IoT) protocol and unified namespace are essential components of Industry 4.0. IoT enables physical devices and systems to collect and exchange data, while a unified namespace ensures seamless communication and information sharing within manufacturing environments. Industry 4.0 can be complex to understand, but it also presents new business opportunities. By embracing digital transformation and adopting IoT protocols, companies can leverage data to drive innovation and gain a competitive edge in the market.
In the following sections, we will explore the concept of Industry 4.0 in greater detail, including the importance of legacy systems, IoT protocols, and a unified namespace. We will provide practical steps to help you start your Industry 4.0 journey. Let’s dive in and discover how IoT Industry 4.0 can revolutionize your business.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, which is characterized by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. It represents a shift towards automation, connectivity, and data exchange in the manufacturing industry. In simple terms, Industry 4.0 is the journey towards digital transformation in business operations. It involves moving away from traditional paper-based processes and adopting advanced technologies to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
One of the critical components of Industry 4.0 is the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT enables the collection and exchange of data between physical devices and systems. This data can then be analyzed to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. The goal of Industry 4.0 is to create a more connected and intelligent manufacturing ecosystem. By leveraging IoT and other digital technologies, businesses can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. The concept of Industry 4.0 also emphasizes the importance of a unified namespace. This means that all devices, systems, and processes within a manufacturing environment should have a standardized way of communicating and sharing information. This ensures seamless integration and interoperability between different components. To embark on the Industry 4.0 journey, businesses must embrace digital transformation and adopt IoT protocols. By doing so, they can harness the power of data and leverage it to drive innovation and gain a competitive edge in the market.
We are all data companies!
In the era of Industry 4.0, the phrase “We are all data companies” holds for businesses of all sizes and industries. With the advent of IoT and the interconnectedness of devices, data has become a valuable asset that can drive innovation and growth. Every business, regardless of its core offering, generates and collects data.

From customer interactions to supply chain operations, data is being developed at an unprecedented rate. However, the real value lies in how businesses leverage this data to gain insights and make informed decisions. By harnessing the power of data, companies can uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that were previously hidden. This enables them to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and deliver better products and services to their customers. For example, retailers can analyze customer purchasing behavior to personalize marketing campaigns, while manufacturers can use data to predict maintenance needs and prevent costly downtime. A data company goes beyond just collecting and analyzing data. It requires a mindset shift towards data-driven decision-making. You need to invest time in understanding your data. Who needs what data in the organization, and when? In the age of Industry 4.0, data is the lifeblood of businesses. Embracing the role of a data company and effectively utilizing data can unlock new opportunities for you and drive success in the digital economy.
Legacy Systems
In the era of Industry 4.0, it’s essential to acknowledge the existence of legacy systems. These systems, often remnants of Industry 3.0, were characterized using Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) on the production floor. These PLCs typically operated on proprietary protocols, enabling communication between controllers. The communication within legacy systems can be categorized into two types: deterministic and non-deterministic systems. Deterministic control systems are still essential for the production floor, ensuring the reliable operation of critical sensors and controls. For example, emergency stops and other safety measures are scanned multiple times per second by the local PLC.
When it comes to data collection from numerous local PLCs, a non-deterministic computer program is typically employed. This program utilizes proprietary protocols to communicate with the controllers. The data collection is often performed on a cyclic scan, occurring a few times per second or minute. While legacy systems continue to play a role in many industries, it’s essential to recognize their limitations in the context of Industry 4.0. These systems may lack the interoperability and scalability required for seamless integration with IoT technologies. However, with the right approach and strategic planning, businesses can bridge the gap between legacy systems and the advancements of Industry 4.0. By leveraging IoT solutions and protocols, companies can gradually modernize their legacy systems, unlocking new possibilities for data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency. The following section will explore the importance of IoT protocols in the context of Industry 4.0.
IoT Protocol
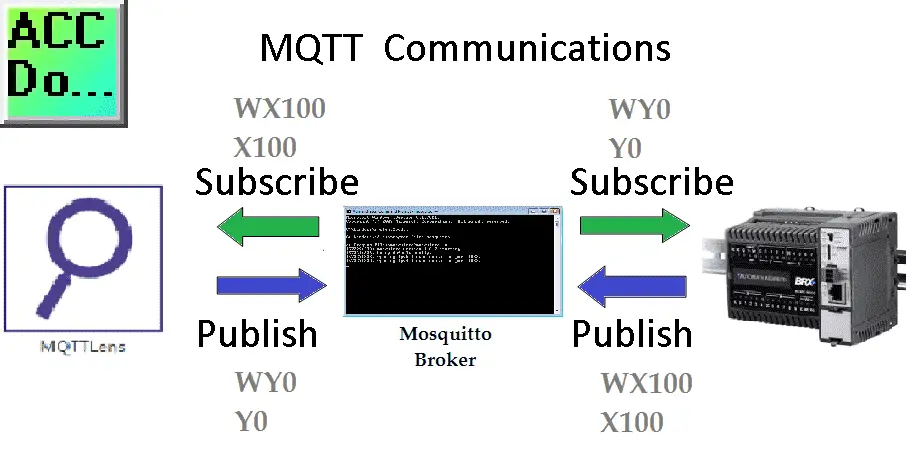
When it comes to the protocol used for the Internet of Things (IoT), there has been much discussion and debate. In my opinion, the ideal protocol should have a low overhead and be capable of utilizing a unified namespace. That’s why I would choose MQTT.
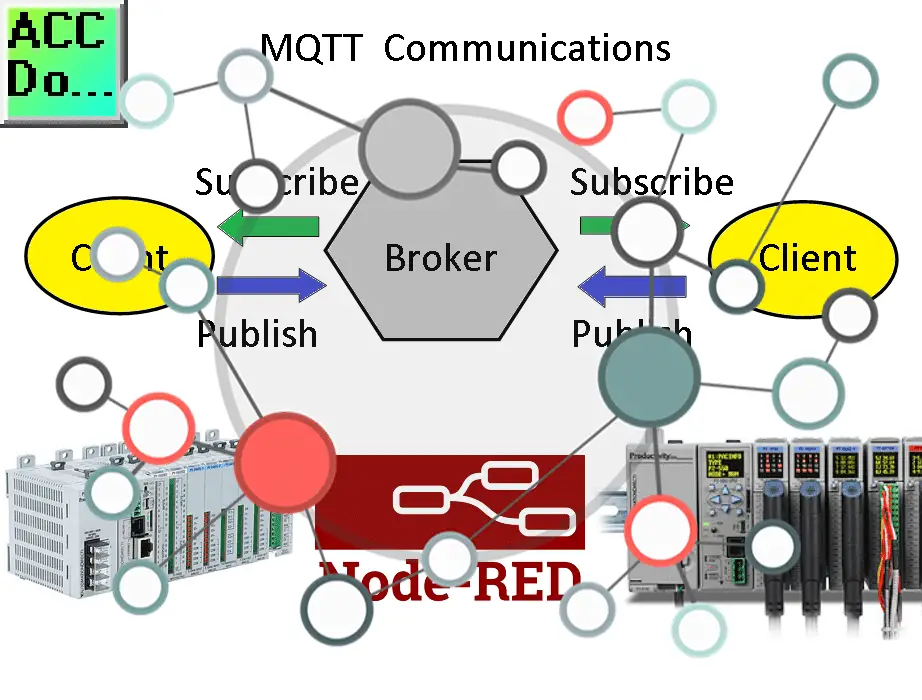
MQTT, or Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, is a report by exception protocol. This means that instead of constantly polling the network for the status of sensors, MQTT only reports when a sensor’s state changes. This approach significantly reduces traffic on your communication line, making it more efficient and scalable.
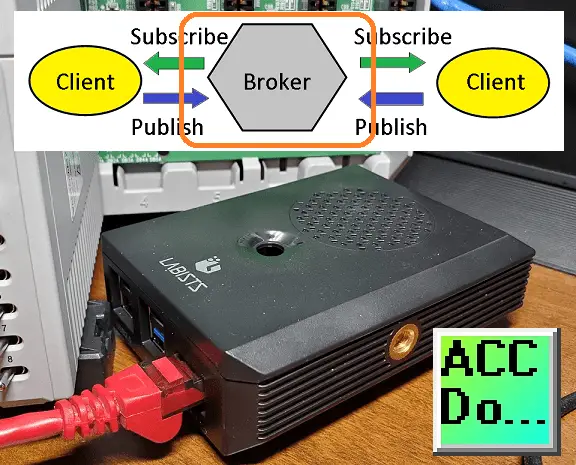
By using MQTT, you can ensure that your IoT system operates with low latency and minimal network congestion. This is especially important in Industry 4.0, where real-time data and responsiveness are crucial for optimizing operations. Another advantage of MQTT is its ability to support a unified namespace.

We will discuss this in the next section. Choosing the proper IoT protocol is essential for the success of your Industry 4.0 initiatives. MQTT’s low overhead and support for a unified namespace make it a strong contender for enabling seamless communication and data exchange in your IoT ecosystem.
Unified Namespace
A unified namespace is a crucial aspect of IoT systems, enabling seamless integration and management of devices. With a unified namespace, you can access and manage items (Edge devices) regardless of type or location, using a single naming convention. This simplifies the process of scaling and expanding your IoT system as needed. To better understand the concept, let’s consider a simple example. Imagine a sensor that measures temperature and humidity in the production area of a plant. With a unified namespace, you can assign a name like “Plant 1/Production Area 3/Sensor 1/Parameters/Temperature” or “Plant 1/Production Area 3/Sensor 1/Parameters/Humidity” to this sensor. Once connected to the system, any control or device can easily read these values without everything being programmed.
By implementing a unified namespace, you create a scalable and flexible system that can accommodate new sensors or devices without the hassle of reprogramming every controller. This streamlines the integration and management of IoT devices, making it easier to adapt and optimize your operations. In the context of Industry 4.0, where data-driven decision-making and real-time responsiveness are crucial, a unified namespace is vital in enabling efficient communication and data exchange within your IoT ecosystem.
How to get started now!
When it comes to implementing IoT in your business, planning is critical. Take the time to understand the data that is being generated and how it is currently being utilized. This will help you identify areas where IoT can bring the most value and efficiency to your operations. Starting small is also an intelligent approach. You don’t have to invest much money upfront to get started with IoT. Instead, implement basic IoT functionalities and gradually expand as you see the benefits. This allows you to test the waters and adjust without a large-scale implementation.
One cost-effective way to get started is by utilizing the Do-More Designer PLC Simulator with MQTT communication to Node-RED. These software packages are 100% free and can serve as a great starting point for your IoT journey.
Node-RED can act as the broker for your IoT system, facilitating communication between devices and enabling data exchange. Following these steps and taking advantage of free resources, you can begin your IoT implementation without breaking the bank.

Remember, the key is to start small, plan effectively, and gradually expand as you gain more experience. You will see the benefits of IoT in action for your movement toward Industry 4.0.
Watch on YouTube: IoT Industry 4.0 Implementation and You
Get started now with the following free software packages:
Do-More Designer Programming Software – PLC Simulator
Node-RED – MQTT Broker / MQTT Subscriber/Publisher
Here are the controllers that we have covered or are covering at ACC Automation:
Arduino Opta PLC
BRX Do-More Series (Do-More Designer Software + Simulator)
Productivity Series P1000 / P2000
Click PLC Series
Omron CP1H Series
Horner XL4 PLC Series
EasyPLC Software Suite is a complete PLC, HMI, and Machine Simulator Software package. See below to receive 10% off this software. This PLC learning package includes the following:
Easy PLC – PLC Simulation will allow programming in Ladder, Grafcet, Logic Blocks, or Script.
HMI System – Easily create a visual human-machine interface (HMI)
Machine Simulator – A virtual 3D world with real-time graphics and physical properties. PLC programs can be tested using the EasyPLC or through other interfaces. (Modbus RTU, TCP, etc.)
Machine Simulator Lite – Designed to run on Android Devices.
Machine Simulator VR – Virtual Reality comes to life so you can test, train, or practice your PLC programming.
Purchase your copy of this learning package for less than $75 USD for a single computer install or less than $100 USD to allow different computers.
Receive 10% off the investment by typing in ACC in the comment section when you order.
Learn PLC programming the easy way. Invest in yourself today.
PLC Beginner’s Guide to PLC Programming
There are many different PLC manufacturers with other hardware and software. All of the programmable logic controllers have similar basic features. Here is how I would approach learning about basic PLCs.
Once you are familiar with the basics of the PLC, you will then learn specifics for the controller you will be programming.
This is the easiest way to learn about PLC programming.
Additional examples of PLC program development using the five steps.
Click PLC – Easy Transfer Line Programming – Video
Productivity PLC Simulator – Chain Conveyor MS – Video
Five Steps to PLC Program Development – Die Stamping
PLC Programming Example – Process Mixer
PLC Programming Example – Shift Register (Conveyor Reject)
PLC Programming Example – Paint Spraying
PLC Programming Example – Delay Starting of 7 Motors
PLC Programming Example – Pick and Place
PLC Programming Example – Sorting Station (Shift Register)
PLC Programming Example – Palletizer
If you have any questions or need further information, please contact me.
Thank you,
Garry
If you’re like most of my readers, you’re committed to learning about technology. Numbering systems used in PLCs are not challenging to learn and understand. We will walk through the numbering systems used in PLCs. This includes Bits, Decimals, Hexadecimal, ASCII, and Floating Points.
To get this free article, subscribe to my free email newsletter.
Use the information to inform other people how numbering systems work. Sign up now.
The ‘Robust Data Logging for Free’ eBook is also available as a free download. The link is included when you subscribe to ACC Automation.


