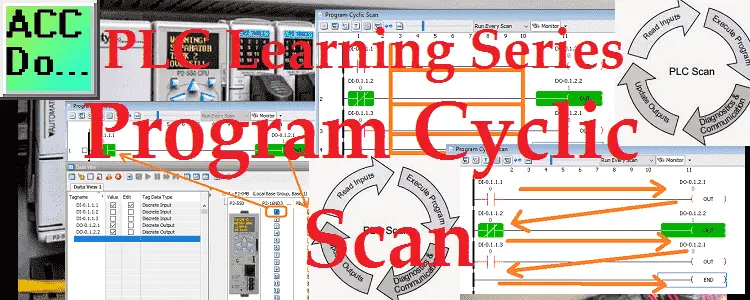
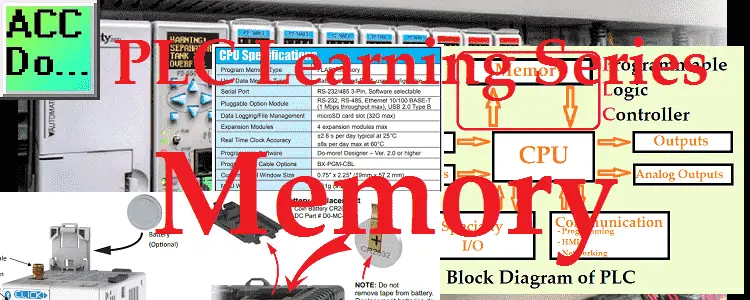
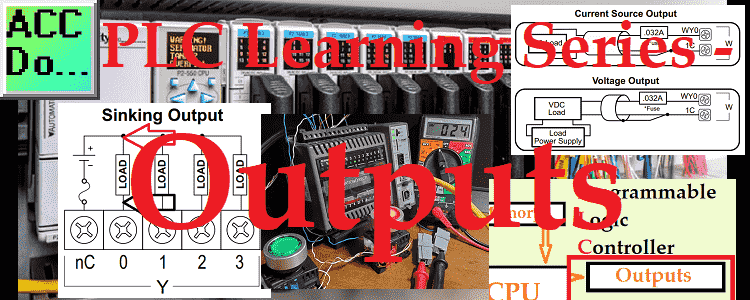
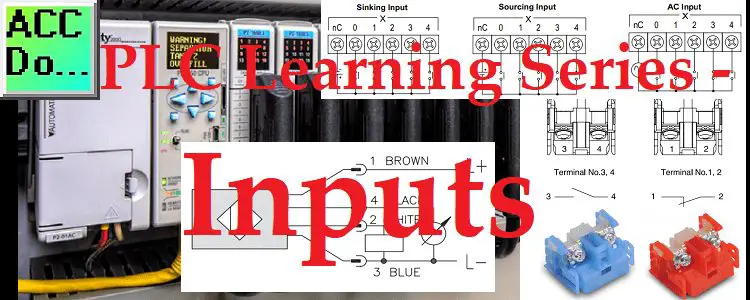
PLC Learning Series – HMI – Interfacing
A human-machine interface (HMI) is present in some form for every PLC. The HMI connects a user to a machine system to exchange information or control data. This interaction with the system can be through hardware or software. HMIs offer different people information and control in many ways for the automated system. Operators, supervisors, mechanics, … Read more